3D printing – or additive manufacturing as it’s known within the industry – is the construction of a three-dimensional model from a digital file. It’s long been in use as a prototyping tool, and a technology for hobbyists to play around with – predominantly printing using thermoplastics. But as the tech has advanced, use cases have expanded.
Printing Buildings?
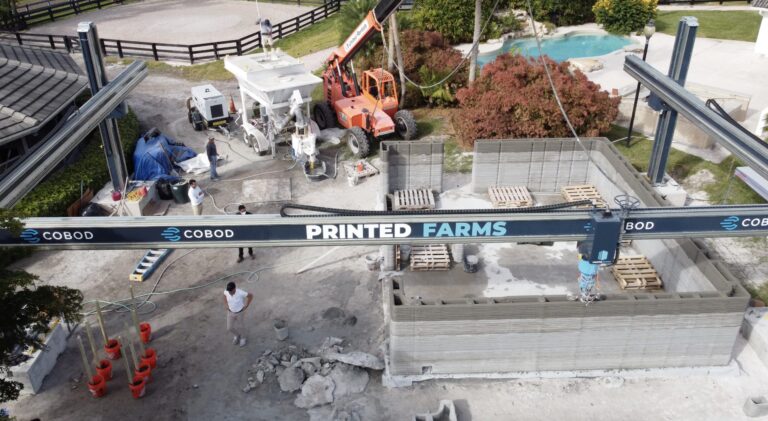
Printed Farms wants to disrupt the construction industry, and were responsible for creating the first 3D-printed building in Europe. The company’s BOD2 is the fastest printer of its type, and can print using real concrete.

Printing Metal
German startup One Click Metal is – as its name suggests – aiming to make 3D metal printing accessible to all. While metal printing is used in large-scale manufacture, it’s currently our of reach for SMEs, entrepreneurs or educators. The company’s printers resembled vending machines, using a powder and cartridge system to create components for everything from watches and jewellery, to motorsports or aerospace engineering.
“Toolmaking, mechanical engineering, education, research – metal 3D printing has many applications.”
And additive manufacturing could be another potential solution to the ongoing supply chain crisis. Mobile Smart Factory aims to support local manufacturing and provide parts on demand. Their solution is fully-functional ‘mini-factories’ built into shipping containers – supremely portable, but able to handle the full manufacturing process from end-to-end.
What Can This Lead to?
3D printing is maturing – with new materials, greater speed, lower costs and more convenience. For larger manufacturers this means efficiency gains, and for smaller companies it means access to a technology that was previously out of reach. No need for a factory any more – just hit ‘print’.