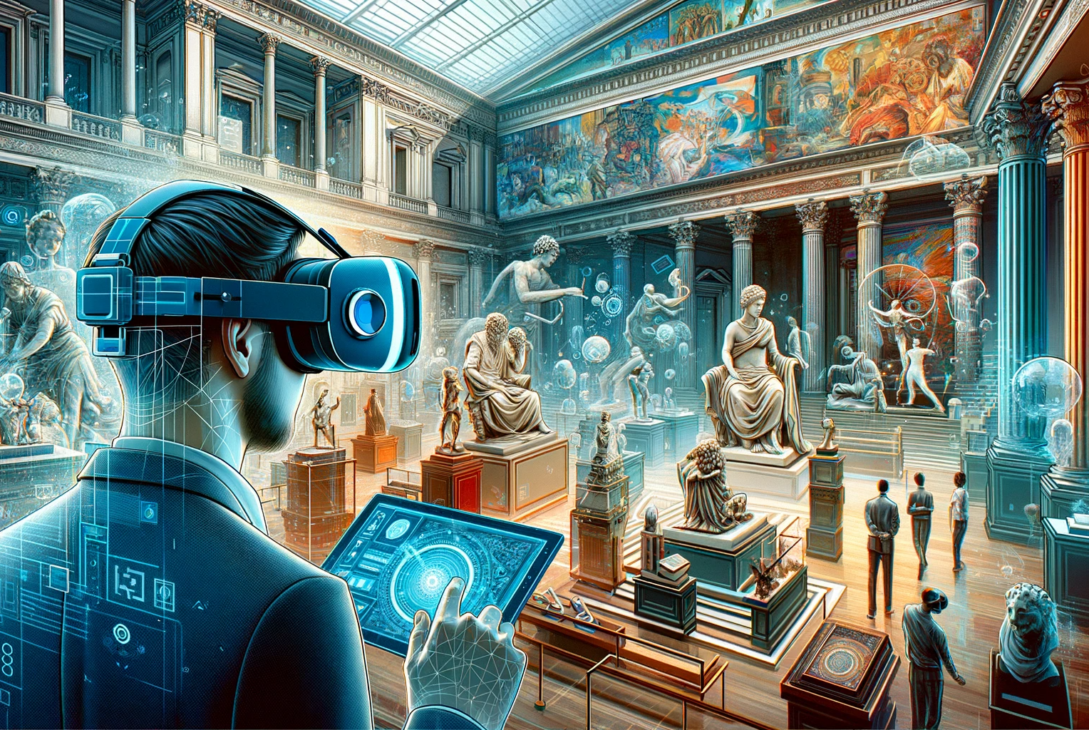
Explore the fascinating intersection of technology and history in our in-depth analysis of VR museums. “The VR Museum Paradox: Is Digital Replication Authentic?” delves into the technical wonders and challenges of recreating historical artifacts and exhibits in immersive virtual reality, examining their educational potential and the quest for authenticity in digital replication.
The emergence of Virtual Reality (VR) has revolutionized many sectors, and the world of museums and historical preservation is no exception. VR offers the tantalizing possibility of creating immersive, detailed replicas of artifacts, exhibits, and entire historical settings. This technology promises to democratize access to cultural heritage, enabling people from all over the world to experience treasures that were previously limited to those who could physically visit certain locations. However, this brings forth a significant question: does digital replication in VR offer an authentic experience, or does it create a synthetic shadow of the real thing?
The Process of Digital Replication in VR
Replicating artifacts and historical exhibits in VR involves a complex interplay of several technologies. The first step is digitization, which usually involves high-resolution 3D scanning and photography. Advanced techniques like photogrammetry and laser scanning are employed to capture the minutest details of an object or site. These techniques create a digital 3D model that serves as the foundation for the VR experience.
Once the artifact is digitized, the next step involves rendering these models in a VR environment. This is where the prowess of VR technology comes into play. Using sophisticated software, these 3D models are brought to life within immersive virtual environments. Lighting, texture, and interactive elements are added to enhance the realism of the experience.
The Educational Value of VR Museums
One of the most significant advantages of VR museums is their educational potential. VR experiences can transcend the limitations of physical space and time. Students and enthusiasts can virtually visit historical sites and examine artifacts that are otherwise inaccessible due to geographical or conservation constraints. This immersive experience can foster a deeper understanding and appreciation of history and culture.
Moreover, VR allows for the presentation of historical contexts in a more engaging and interactive manner. For instance, a VR tour of an ancient city can include dynamic reconstructions of daily life scenes, offering a more vivid and relatable understanding of the past. This aspect of VR can particularly enhance the learning experience for younger audiences, who are more receptive to digital and interactive forms of education.

Ensuring Authenticity in Digital Replicas
The pursuit of authenticity in digital replicas is a challenging technical endeavor. The accuracy of a VR replica hinges on the resolution and precision of the digitization process. High-resolution scans must capture not only the shape and size of the artifacts but also the texture, color, and even the wear and tear that they have endured over time.
To achieve this, VR developers collaborate closely with historians, archaeologists, and conservators. These experts provide essential insights into the historical context and physical characteristics of the artifacts, ensuring that the digital replicas are as accurate as possible. However, despite these efforts, a digital replica can never fully capture the essence of an artifact. The tactile experience, the sense of scale, and the ambiance of a physical museum space are challenging to replicate fully in a virtual environment.
Technical Challenges in VR Replication
Creating accurate and authentic VR replicas of historical artifacts and exhibits is fraught with technical challenges. One of the primary issues is the limitation of current VR technology in terms of resolution and realism. While VR headsets and graphical capabilities have improved significantly, there is still a gap between the virtual and the real, especially when it comes to detailed textures and the play of light on different surfaces.
Another challenge is the digital preservation of these VR experiences. As technology evolves, ensuring that today’s digital replicas are compatible with future VR systems is crucial. There is also the issue of data storage and management. High-resolution 3D models require substantial storage space and robust data management systems to ensure their long-term preservation.
Advanced Technologies in VR Museum Experiences
The creation of a VR museum experience goes beyond basic 3D modeling. Cutting-edge technologies like Augmented Reality (AR), Mixed Reality (MR), and Artificial Intelligence (AI) play crucial roles. AR and MR can be used to overlay digital information onto real-world museum settings, providing an enhanced educational experience. AI, on the other hand, can be employed to create interactive and responsive environments within the VR setting. AI algorithms can analyze user interactions and preferences to personalize the museum experience, making it more engaging and informative.
Moreover, haptic feedback technology is being integrated into VR experiences to provide tactile sensations, bridging the gap between the digital and the physical. This technology can simulate the texture and weight of artifacts, offering a more immersive and realistic experience.
Technical Intricacies in VR Experience Creation
Creating a VR museum experience is not just about replicating the visual aspect of artifacts and exhibits. It involves recreating the ambiance and context in which these artifacts originally existed. This requires meticulous attention to historical accuracy in terms of lighting, environmental sounds, and even the weather conditions of a particular era or location.
Furthermore, the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) design in VR museums are critical. They must be intuitive and accessible to people of all ages and technological expertise. Navigating a VR museum should be a seamless experience, free from technical glitches and overwhelming controls.
Data Accuracy and Detailing
Ensuring data accuracy in digital replicas is paramount. This not only involves the physical attributes of the artifacts but also their historical significance and context. Collaborations with historians, archaeologists, and cultural experts are vital to maintain the integrity and educational value of these VR experiences.
Detailing in VR museums extends to the minutest aspects.
For instance, the wear patterns on a centuries-old vase or the fading colors on an ancient manuscript must be accurately represented to provide a realistic experience. This level of detailing requires immense computational power and sophisticated software capable of rendering high-resolution textures and complex geometries.
The Future of VR Museums
Looking ahead, the future of VR museums is promising and full of potential. With the rapid advancement of VR technology, we can expect more realistic and immersive experiences. One exciting development is the incorporation of real-time environmental interaction, where users can experience changes in the museum setting depending on the time of day or weather conditions, just like in the real world.
Another potential development is the use of VR for reconstructing lost or damaged artifacts and sites. VR can be a tool for digital preservation, where artifacts at risk of deterioration can be preserved in their current state and restored virtually for educational purposes.
Moreover, as VR technology becomes more affordable and accessible, we can expect a democratization of cultural experiences. People from remote or underprivileged areas will have the opportunity to explore museums and cultural sites from around the world, breaking down barriers of geography and socio-economic status.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the replication of historical artifacts and exhibits in VR represents a blend of art, science, and technology. While it poses significant technical challenges, from ensuring historical accuracy to creating immersive and realistic experiences, the potential it holds for education and cultural preservation is immense. As technology evolves, so will the capabilities of VR museums, offering more authentic, interactive, and personalized experiences to users worldwide.
The VR Museum Paradox, therefore, lies in the balance between digital replication and authenticity. While a digital replica can never fully replace the experience of viewing an artifact in person, the educational and cultural value it adds, especially in a world increasingly reliant on digital technologies, is undeniable.